
Back Jakobson se taalfunksies Afrikaans Funciones del llinguaxe AST Funcions del llenguatge Catalan Roman Jakobsons kommunikationsmodel Danish Sprachfunktion German Funciones del lenguaje Spanish Jakobsoni kommunikatsioonimudel Estonian Schéma de Jakobson French Función da linguaxe Galician תפקודי הלשון על פי יאקובסון HE
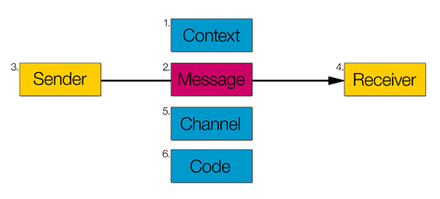
Roman Jakobson defined six functions of language (or communication functions), according to which an effective act of verbal communication can be described.[2] Each of the functions has an associated factor. For this work, Jakobson was influenced by Karl Bühler's organon model, to which he added the poetic, phatic and metalingual functions.
- ^ Middleton, Richard (April 1, 1990). Studying Popular Music. Philadelphia, UK: McGraw-Hill Education. p. 241. ISBN 0-335-15275-9.
- ^ Waugh, Linda R. (1980). "The Poetic Function in the Theory of Roman Jakobson". Poetics Today. 2 (1). Duke University Press: 57–82. doi:10.2307/1772352. JSTOR 1772352.